
NATO and USAF reporting names were as follows:
* MiG-15 (NATO reporting name "Fagot"), (USAF/DoD reporting name "Type 14".
* MiG-15P (NATO reporting name "Fagot"), (USAF/DoD reporting name "Type 19".
* MiG-15UTI (NATO reporting name "Midget"), USAF/DoD reporting name "Type 29".
Design and development
Most early jets were designed like piston-engined fighters with straight wings, limiting their high speed performance. German research during World War II had shown swept wings would perform better at transonic speeds, and Soviet aircraft designers were quick to take advantage of this information. Claims of Artem Mikoyan and Mikhail Gurevich (lead designers of the "MiG" bureau) being heavily influenced by the Focke-Wulf Ta 183, however, have been discredited. Although the abortive late-war German jet had swept wings and bore a superficial resemblance to the later MiG-15, the two aircraft are very different in structure and general design. The Soviets did seize plans and prototypes for the Ta-183, but the majority of Focke-Wulf engineers were captured by Western armies, therefore it could be argued that the MiG-15 design team drew some limited inspiration from the Ta-183, but there is insufficient evidence to suggest it was heavily influenced by the Ta-183. Currently, most sources acknowledge that the MiG-15 is an original design benefiting from German research, but conceived, designed, engineered, and produced by the Soviets.
The unusual MiG-8 Utka experimental canard aircraft, built right at the conclusion of World War II by the MiG design bureau, is said to have also been a major influence in the use of swept wings on later Mikoyan designs.
By 1946, Soviet designers were finding it impossible to perfect the German-designed HeS-011 axial-flow jet engine, and new airframe designs from Mikoyan were threatening to outstrip development of the engines to power them. Soviet aviation minister Mikhail Khrunichev and aircraft designer A. S. Yakovlev suggested to Premier Joseph Stalin the USSR buy advanced jet engines from the British. Stalin is said to have replied, "What fool will sell us his secrets?"
However, he gave his consent to the proposal and Mikoyan, engine designer Vladimir Klimov, and others travelled to the United Kingdom to request the engines. To Stalin's amazement, the British Labour government and its pro-Soviet Minister of Trade, Sir Stafford Cripps, were perfectly willing to provide technical information and a license to manufacture the Rolls-Royce Nene. This engine was reverse-engineered and produced as the Klimov RD-45, subsequently incorporated into the MiG-15. Rolls-Royce later attempted to claim £207 million in license fees, without success.[citation needed]
In the interim, on 15 April 1947, the Council of Ministers issued decree #493-192, which ordered the Mikoyan OKB to build two prototypes for a new jet fighter. As the decree called for a first flight as soon as December, designers at OKB-155 fell back on an earlier troublesome design, the MiG-9. The MiG-9 suffered from an unreliable engine and control problems; the first would be solved by the excellent new Klimov engine, and to solve the second, the designers began experimenting with swept wings and redesigning the tail. The resulting prototypes were designated I-310.
The I-310 was a clean, swept-wing fighter with 35° sweep in wings and tail, and exceptional performance, with a top speed of over 1,040 km/h (650 mph). Its primary competitor was the similar Lavochkin La-168. After evaluation, the MiG design was chosen for production. Designated MiG-15, the first production example flew on 31 December 1948. It entered Soviet Air Force service in 1949, and would subsequently receive the NATO reporting name "Fagot." Early production examples had a tendency to roll to the left or right due to manufacturing variances, and so aerodynamic trimmers called "nozhi (knives)" were fitted to correct the problem, the knives being adjusted by ground crews until the aircraft flew correctly.
An improved variant, the MiG-15bis ("second"), entered service in early 1950 with a Klimov VK-1 engine, an improved version of the RD-45/Nene, plus minor improvements and upgrades. Visible differences are: a headlight in the air intake separator and horizontal upper edge airbrakes. The 23 mm cannons were placed more closely together in their undercarriage. Some "bis" aircraft also adopted under-wing hardpoints for unguided rocket launchers or 50-250 kg (110-551 lb) bombs. Fighter-Bomber modifications were dubbed "IB", "SD-21", and "SD-5". About 150 aircraft were upgraded to SD-21 specification during 1953–1954. An unknown number of aircraft were modified to "IB" specification in the late 1950s.
The MiG-15 arguably had sufficient power to dive at supersonic speeds, but could not do so because it did not feature a "all-flying" tail. As a result, the pilot's ability to control the aircraft deteriorated significantly as it approached Mach 1. Later MiGs would incorporate all-flying tails.
The MiG-15 was originally intended to intercept American bombers like the B-29. It was even evaluated in mock air-to-air combat trials with a captured U.S. B-29, as well as the later Soviet B-29 copy, the Tu-4 "Bull". To ensure the destruction of such large bombers, the MiG-15 carried cannon armament: two 23 mm with 80 rounds per gun and a single 37 mm with 40 rounds. These weapons provided tremendous punch in the interceptor role, but their limited rate of fire and relatively low velocity made it more difficult to score hits against small and maneuverable enemy jet fighters in air-to-air combat. The 23 mm and 37 mm also had radically different ballistics, and some United Nations pilots in Korea had the unnerving experience of 23 mm shells passing over them while the 37 mm shells flew under. The cannon were fitted into a neat pack that could be winched down out of the bottom of the nose for servicing and reloading, in principle allowing a preprepared pack to be switched for rapid turnaround. (Some sources mistakenly claim the pack was added in later models.)
A variety of MiG-15 variants were built, but the most common was the MiG-15UTI (NATO reporting name Midget) two-seat trainer.
Because Mikoyan-Gurevich never mass-produced the transition training versions of the later MiG-17 or MiG-19, the MiG-15UTI remained the sole Warsaw Pact advanced jet trainer well into the 1970s, the primary training role being fulfilled exclusively by Czechoslovak Aero L-29 Delfin and the L-39 Albatros jet trainers (save for Poland, which used their indigenous TS-11 Iskra jets). While China produced two-seat trainer versions of the later MiG-17 and MiG-19, the Soviets felt that the MiG-15UTI was sufficient for their needs and did not produce their own trainer versions of those aircraft.
Operational history

The MiG-15 was widely exported, with the People's Republic of China receiving MiG-15bis models in 1950. Chinese MiG-15s took part in the first jet-versus-jet dogfights after communist North Korea's invasion of South Korea. The swept-wing MiG-15 quickly proved superior to the first-generation, straight-wing jets of the United Nations air forces, such as the F-80 and Gloster Meteor, as well as piston-engined P-51 Mustangs and F4U Corsairs (although an American F-80 would score the first all-jet, air-to-air kill in history over a MiG-15). Only the F-86 Sabre, with its highly trained pilots, was a match for the MiG.
Its baptism of fire occurred during the last phases of the Chinese Civil War (1946–49). During the first months of 1950, the aviation of Nationalist China attacked from Taiwan the communist position in continental China, specially Shanghai. Mao Zedong requested the military assistance of the USSR, and the 50th IAD (Russian: Истребительная Авиадивизия, ИАД; Istrebitelnaya Aviadiviziya; Fighter Aviation Division) equipped with the MiG-15bis was deployed south of the People’s Republic of China. On 28 April 1950, Captain Kalinikov shot down a P-38 of the Kuomitang, scoring the first aerial victory of the MiG-15. Another followed on 11 May, when Captain Ilya Ivanovich Schinkarenko downed the B-24 Liberator of Li Chao Hua, commander of the 8th Air Group of the nationalist Air Force.
The Korean War (1950-1953)
The North Koreans began their war against South Korea on 25 June 1950 with World War II-vintage Soviet prop-driven fighters, including 93 Il-10s and 79 Yak-9Ps, flown by inexperienced pilots. Once the United States quickly swept the skies clear, led by advanced jets such as F-80 Shooting Star and F-84 Thunderjet fighters, B-29 bombers and Navy and Marine aircraft roamed the skies over North Korea largely unopposed, while the North Koreans and their Soviet and Communist Chinese backers considered the best course of counter-action.
Their decision to introduce the MiG-15 not only closed the jet fighter gap, its performance leapfrogged all of the opposing straight-winged jets. The MiG-15s proved very effective in its designed role against formations of B-29 heavy bombers, shooting down many UN fighter and bomber aircraft. Though American histories record that the F-86 had the advantage in combat kills, the Soviet 64th IAK (Fighter Aviation Corps) claimed 1,106 UN aircraft destroyed in the Korean War, compared to Allied records that 142 Allied aircraft were downed by the Soviet MiG-15 pilots. Western experts do acknowledge many Russian pilots earned bigger individual scores than their American counterparts due to a number of factors, though overall figures from both sides were probably overstated.
For many years, the participation of Soviet aircrews in the Korean War was widely suspected by the United Nations forces, but consistently denied by the Soviet Union. With the end of the Cold War, however, Soviet pilots who participated in the conflict have begun to reveal their role. Soviet aircraft were adorned with North Korean or Chinese markings and pilots wore either North Korean uniforms or civilian clothes to disguise their origins. For radio communication, they were given cards with common Korean words for various flying terms spelled out phonetically in Cyrillic characters. These subterfuges did not long survive the stresses of air-to-air combat, however, and pilots routinely communicated in Russian. Soviet pilots were prevented from flying over areas in which they might be captured lest they give away the Soviet ruse.
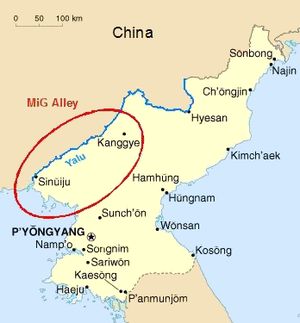
The USSR never acknowledged that their pilots ever flew over Korea during the Cold War. Americans who intercepted radio traffic during combat confirmed hearing Russian voices, but only the Chinese and Koreans took credit for the flying. Until the publishing of recent books by Chinese and Russian authors, such as Xiaoming Zhang, Leonid Krylov, Yuriy Tepsurkaev and Igor Seydov, little was known of the actual pilots. The Americans recognized the skills of their opponents who they called "honchos", and dubbed the northwestern portion of North Korea where the Yalu River empties into the Yellow Sea MiG Alley as the site of numerous dogfights.
The Russians were training Chinese MiG-15 pilots when the Chinese entered the war in support of North Korea. By October, the Soviet Union had agreed to provide air regiments of state-of-the-art Soviet-designed and -built MiG-15 fighters, along with the trained crews to fly them. Simultaneously, the Kremlin agreed to supply the Chinese and North Koreans with their own MiG-15s, as well as train their pilots. On 1 November 1950, eight MiG-15s intercepted about 15 F-51D Mustangs of the United States Air Force (USAF) and First Lieutenant Fiodor V. Chizh shot down the F-51D of Aaron Abercombrie in his MiG-15, killing the American aviator. Three MiG-15s of the same unit intercepted 10 F-80 Shooting Stars, and the MiG-15 of First Lieutenant Semyon Fiodorovich Jominich scored the first jet-vs-jet victory in history when he bagged the F-80C of Frank Van Sickle, who would also perish (USAF credits both losses to the action of the North Korean flak).[11] However on 9 November, the Soviet MiG-15 pilots suffered their first loss when Lieutenant Commander William T. Amen off the aircraft carrier USS Philippine Sea shot down and killed Captain Mijail F. Grachev while flying a F9F Panther.
The Soviet air units claimed to have shot down 29 American aircraft through the rest of the month: 11 F-80s, seven B-29s and nine F-51s. 23 out of these 29 claims match with acknowledged losses, but the American sources assert that most of them were operational or due to AAA, admitting only four B-29s (a downed B-29, plus two B-29s and a RB-29 which crash-landed or were damaged beyond repair). Both sides agree that the MiG-15 eliminated USAF aerial superiority over northwestern Korea.
To restore the unexpected turn of events, three squadrons of the F-86 Sabre, America's only operational American jet with swept wings were quickly rushed to the Far East in December. [13] On 17 December 1950, the first encounter between these two opponents ended with a clear American victory when Lieutenant Colonel Bruce H. Hinton forced Major Yakov Nikanorovich Yefromeyenko to eject from his burning MiG.[11] In the following days both sides traded punches, with Captain Nikolay Yefremovich Vorovyov shooting down the F-86A of Captain Lawrence V. Bach in the cockpit of his MiG-15bis on 22 December 1950. [11] Both sides exaggerated the their claims of aerial victories that month; the Sabre fliers claimed eight MiGs, and the Soviets claimed to have shot down 12 F-86s. The actual losses were three MiGs and at least one Sabre (the total might be four).
Those first encounters established the main features of the aerial battles of the next two and a half years. The MiG-15 and MiG-15bis had a higher ceiling than all the versions of the Sabre – 15,700 m (51,509 ft) versus 14,200 m (46,588 ft) of the F-86F – and accelerated faster than F-86A/E/Fs due to their better thrust-to-weight ratio – 1,005 km/h (624 mph) versus 972 km/h (604 mph) of the F-86F. The MiG-15's2,800 m (9,186 ft) per minute climbing rate was also greater than the 2,200 m (7,218 ft) per minute of the F-86A and -E (the F-86F matched the MiG-15s rate). A better turn radius above 10,000 m (32,808 ft) further distinguished the MiG-15, as did more powerful weaponry – one 37 mm NR-37 cannon and two 23 mm NR-23 cannons, versus the inferior hitting power of the six 12.7 mm (.50 in) machine guns of the Sabre. But the MiG was slower at low altitude – 935 km/h (581 mph) in the MiG-15bis configuration as apposed to the 1,107 km/h (688 mph) of the F-86F. The Soviet World WarII-era ASP-1N gyroscopic gunsight was less sophisticated than the accurate A-1CM and A4 radar ranging sights of the F-86E and -F. All Sabres turned tighter below the 8,000 m (26,247 ft) of altitude.
Thus if the MiG-15 forced the Sabre to fight in the vertical plane, or in the horizontal one above 10,000 m (32,808 ft), it gained a significant advantage. Furthermore, the pilot of a MiG-15 could easily escape from a Sabre by climbing to its ceiling, knowing that the F-86 could not follow him. Below 8,000 m (26,247 ft) however, the Sabre excelled over the MiG in almost every aspect excluding the climb rate and was the victor most of the time, especially if the Soviet pilot made the mistake of fighting in the horizontal plane.
The main mission of the MiG-15 was not to dogfight against the F-86s however, but to counter the USAF B-29 Superfortress bombers. This mission was assigned to the elite of the Soviet Air Force (VVS), in April 1951 to the 324th IAD of Colonel Ivan Kozhedub, and later to the 303rd IAD of General Georgiy A. Lobov, who arrived to Korea in June of that same year.
44 MiG-15s achieved victories in that mission on 12 April 1951 when they intercepted a large formation of 48 Superfortresses, 18 Sabres, 54 F-84 Thunderjets and 24 F-80 Shooting Stars heading towards the bridge linking North Korea and China over the Yalu river in Uiju. When the ensuing battle was finished, the experienced Soviet fliers had shot down or damaged beyond repair ten B-29As, one F-86A and three F-80Cs with the loss of only one MiG.
The American strategic bombers returned the week of 22-27 October to neutralize the North Korean aerodromes of Namsi, Taechon and Saamchan, taking further losses to the MiG-15. On 23 October 1951, 56 MiG-15bis intercepted nine Superfortresses escorted by 34 F-86s and 55 F-84Es. In spite of their numerical inferiority the Soviet airmen shot down or damaged beyond repair eight B-29As and two F-84Es, losing only one MiG in return and leading Americans to call that day Black Tuesday[citation needed]. The most successful Soviet pilots that day were Lieutenant Colonel Aleksandr P. Smorchkov and 1st Lieutenant Dmitriy A. Samoylov. The former shot down a Superfortress on each of 22, 23 and 24 October. Samoylov added two F-86As onto his scoreboard on 24 October 1951, and on October 27 shot down two more aircraft: the a B-29A and an F-84E. These losses among the heavy bombers forced the FEAF’s[clarification needed] High Command to cancel the precision daylight attacks of the B-29s, and only perform radar directed night raids.
During the period from November 1950 to January 1952 no less than 40 Soviet MiG-15 pilots were credited as aces, with five or more victories in their respective tallies. Soviet combat records show that the first pilot to claim his fifth aerial victory was Captain Stepan Ivanovich Naumenko on 24 December 1950. However, crossing references with the USAF loss records, it seems that his actual tally was only three kills (one B-29A, one F-86A and one F-84E). Neither was the first ace of the Korean War James Jabara, proclaimed ace on 20 May 1951 as only four out of six claims can be confirmed. The honor falls to Captain Sergei Kramarenko, when on 29 July 1951, he scored his actual fifth victory. No less than 16 out of those 40 pilots actually became aces, the most successful being Major Nikolay Sutyagin, credited with 22 victories, 13 of which can be confirmed; Colonel Yevgeny Pepelyaev with 19 claims, 15 actual victories; and Major Lev Shchukin - 17 credited, 11 verified.
In spite of the successful performance of those divisions, by late January 1952 the High Command of the Armed Forces of the USSR decided to replace them with two new units of the PVO (Russian: Противо Воздушная Oборона, ПВО; Protivo Vozdúshnaya Oborona; Anti-Aircraft Defense). This proved to be a mistake, as such units were trained to intercept bombers with nuclear weapons, not to dogfight against the F-86s. Furthermore, unlike the divisions they replaced, which were made up almost completely of veterans of World War II, only the commanders and staff of the incoming 97th and 190th IAD had combat experience during World War II, with the bulk of the fliers having only 50-60 hours flying the MiG.
Consequently those units suffered great losses by the now better prepared American Sabre pilots. During the six months of February to July 1952 they lost 81 MiGs and 34 pilots were killed by F-86s, and in return they only shot down 68 US aircraft (including 36 F-86s). The greatest losses came on 4 July 1952, when 11 MiGs were downed by the Sabres, with one pilot killed in action. Contributing to all this was the secret and illegal "Maple Special" Operation, a plan by the WWII ace Colonel Francis Gabreski to cross the Yalu river into Manchuria (something officially forbidden) and catch the MiGs unaware during their takeoffs or landings, when they were at disadvantage: flying slow, at a low level, and sometimes short of ammunition and fuel. Even under these circumstances, MiG-15 pilots would score at least two important victories against American aces:
- 10 February 1952: 1st Lieutanant. Mikhail Akimovich Averin shot down and killed the ace Major George Andrew Davis, Jr. (credited with 14 victories at the moment of his death, 10 confirmed by the Communist sources).
- 4 July 1952: A few seconds after shooting down 1st Lieutenant. M. I. Kosynkin, future ace Captain Clifford H. Jolley was forced to eject out of his crippled F-86E after being caught by surprise by the MiG-15bis pilot 1st Lieutenant Vasily Romanovich Krutkikh
At least two Soviet fliers became aces during that period: Majors Arkadiy S. Boytsov and Vladimir N. Zabelin with six and nine victories respectively.
New and better trained PVO divisions would replace the beaten 97th and 190th in July and August 1952, and though they could not take the aerial superiority away from the Americans, they could neutralize it between September 1952 and the end of the war[clarification needed]. Again, the figures of victories and losses in the air are still debated by historians of USA and Russia, but on at least three occasions Soviet MiG-15 aces gained the upper hand against Sabre aces:
- 7 April 1953: Shortly after causing damages to a Chinese MiG and a Soviet one over Dapu airbase in Manchuria, the ace of 10 kills Captain Harold E. Fischer was downed by the future ace 1st Lieutenant Grigoriy Nesterovich Berelidze and taken prisoner.
- 12 April 1953: Captain Semyon Alekseyevich Fedorets, a Soviet ace with eight victories, shot down the F-86E of Norman E. Green, but shortly afterward was attacked by the future top American ace of the Korean War, Captain Joseph C. McConnell. In the ensuing dogfight, both aces shot each other down, ejecting and being rescued safely.
- 20 July 1953: During an illegal raid deep into Manchuria, and after shooting down two Chinese MiGs, Majors Thomas M. Sellers and Stephen L. Bettinger (the second an ace with five kills) tried to catch by surprise two Soviet MiG-15s that were landing in Dapu. The Russian fliers skillfully forced the Americans to overshoot, reversed direction and shot both down: Captain Boris N. Siskov forced Bettinger to bail out and his wingman 1st Liuetenant. Vladimir I. Klimov killed Major Sellers. This was the fifth victory of Boris Siskov, making him the last ace of the Korean War. Those were also the last Sabres downed by Soviet fliers during the Korean War.
The MiG-15 threat forced the FEAF to cancel the B-29 daylight raids in favor of night radar-guided missions from November 1951 onwards. Initially this presented a threat to Communist defenses as their only specialized nightfighting unit was equipped with the prop-driven Lavochkin La-11, inadequate for the task of intercepting the B-29. Part of the regiment was re-equipped with the MiG-15bis, and another nightfighting unit joined the fray, causing American heavy bombers began to suffer losses again. Between 21:50 and 22:30 on 10 June 1952 four MiG-15bis attacked Superfortresses over Sonchon and Kwaksan. Lieutenant Colonel Mikhail Ivanovich Studilin damaged a B-29A beyond repair, which made an emergency landing at the Kimpo Air Base. A few minutes later, Major Anatoly Karelin added two more Superfortresses to his tally and Igor Seydov,. Studilin and Karelin's wingmen, Major L. A. Boykovets and 1st Lt. Zhahmany Ihsangalyev, also damaged one B-29 each. Anatoly Karelin eventually became an ace with six kills (all B-29s at night). In the aftermath of these battles, B-29 night sorties were cancelled for two months. Originally conceived to shoot down rather than escort bombers, both of America's state-of-art jet nightfighters - the F-94 Starfire and the F3D Skynight - were committed to protect the Superfortresses against MiGs.
The MiG-15 was less effective in getting past the Marine Corps ground-based two-seat F3D Skyknight night fighters assigned to escort B-29s in darkness after the F-94 Starfires proved ineffective. What the squat planes lacked in sheer performance they made up with the advantage of a search radar which enabled the Skyknight to see its targets clearly while the MiG-15's directions to find bomber formations were of little use to see escorting fighters. On the night of 2–3 November 1952, a Skyknight with pilot Major William Stratton and radar operator Hans Hoagland damaged the MiG-15 of Captain V. D. Vishnyak. Five days later, Oliver R. Davis with radar operator D.F. "Ding" Fessler downed a MiG-15bis; the pilot, Lieutenant Ivan P. Kovalyov, ejected safely. Skyknights claimed five MiG kills with no losses of their own, and no B-29s under their escort were lost to enemy fighters. However the duel was not one-sided: on the night of 16–17 January 1953, an F3D almost did fall to a MiG, when the Skynight of Captain George Cross and Master Sargeant J. A. Piekutowski suffered serious damage in an attack from a Soviet MiG-15bis; with difficulty, the Skynight returned to the Kunsan Air Base. Three and a half months later, on the night of 29–30 May 1953 the Chinese MiG-15 pilot Hou Shujun of the PLA Air Force shot down over Anju a F3D-2; Capt. James B. Brown and Sgt. James V. Harrell, the unfortunate crew, still remain missing in action.
In a Royal Navy Sea Fury flying from a light fleet carrier FAA pilot Lieutenant Peter "Hoagy" Carmichael Royal Navy downed a MiG-15 jet fighter on August 8, 1952, in air-to-air combat. The Sea Fury would be one of the few prop-driven fighter aircraft to shoot down a jet-powered fighter. On September 10, 1951, Capt. Jesse G. Folmar shot down a MiG-15 with an F4U Corsair, but was himself shown down by another MiG.
The figures given by the Soviet sources indicate that the MiG-15s of the 64th IAK (the Fighter Corp which included all the divisions that rotated along the conflict) performed 60,450 daylight combat sorties and 2,779 night ones, engaged the enemy in 1,683 daylight aerial battles and 107 at night, claiming to have shot down 1,097 UN aircraft over Korea, including 647 F-86s, 185 F-84s, 118 F-80s, 28 F-51s, 11 F-94s, 65 B-29s, 26 Gloster Meteors and 17 aircraft of different types. Losses were heavy: 335 airplanes and 120 pilots; 319 MiGs and 110 airmen were lost in combat, the remaining in operational accidents. The statistics of victories are almost certainly inflated (at least by 50%), but also it seems clear that the MiG-15s flown by Soviet personnel caused serious problems to the USAF and their allies in Korea, much more serious of what the traditional American bibliography had acknowledged so far.
The Soviet VVS and PVO were the primary users of the MiG-15 during the war, but not the only ones; it was also used by the People’s Air Forces of China and North Korea (known as the United Air Army). Excluding a brief episode in January 1951, the Chinese Air Force did not see action until 25 September 1951, when 16 MiG-15s engaged Sabres, with the pilot Li Yongtai claiming a victory but losing a MiG and its pilot. The North Korean unit equipped with the MiG-15 got into action a year later, in September 1952. From then until the end of the war the United Air Army claimed to shot down 211 F-86s, 72 F-84s and F-80s, and 47 other aircraft of various types, losing 116 Chinese airmen and 231 aircraft: 224 MiG-15s, three La-11s and four Tupolev Tu-2s. Several pilots were credited with the shootdown of five or more enemy airplanes, such as Zhao Baotong with seven victories, Wang Hai with nine kills; both Kan Yon Duk and Kim Di San were credited with five victories.
Defection
Eager to obtain an intact MiG for testing, the United States offered a reward of US$100,000 and political asylum to any pilot who would defect with his airplane. Eventually, the North Korean pilot Lieutenant No Kum-Sok, who claimed to be unaware of the reward, landed at Kimpo Air Base on 21 September 1953, allowing the first detailed evaluation of the aircraft.
This MiG-15 was minutely inspected and was test flown by several test pilots including Chuck Yeager. Yeager reported in his autobiography the MiG-15 had dangerous handling faults and claimed that during a visit to the USSR, Soviet pilots were incredulous he had dived in it, this supposedly being very hazardous. When this story got back to the Russian pilots Yeager claimed to have talked to, they angrily denounced it. In fact, although the MiG-15 did have some handling quirks and could, in principle, exceed flight limits in a dive, its airbrakes opened automatically at the red line limit, preventing it from going out of control. Lieutenant No's aircraft is now on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force near Dayton, Ohio.
The Cold War
During the 1950s the MiG-15s of the USSR and their allies of the Warsaw Pact intercepted aircraft of the NATO air forces performing reconnaissance near or inside their territory on many occasions; such incidents sometimes ending with airplanes of one side or the other being shot down. The known incidents where the MiG-15 was involved follow (Sources: "Air Aces - Shootdowns of the Cold War Era, "Goryachoe Nebo Kholodnoy Voyny" ("The Hot Sky of the Cold War" (in Russian)) and Aircraft Downed During the Cold War and Thereafter).
- 16 December 1950: An RB-29 of USAF is downed over Primore (Sea of Japan) by two MiG-15 pilots, Captain Stepan A. Bajaev and 1st Lieutenant N. Kotov.
- 19 November 1951: MiG-15bis pilot, 1st Lieutenant. A. A. Kalugin forces a USAF C-47 that had penetrated Hungarian airspace to land at the airbase at Pápa.
- 13 June 1952: two naval MiG-15s flown by Captain Oleg Piotrovich Fedotov and 1st Lieutenant Ivan Petrovich Proskurin shot down a RB-29A of near Valentin Bay, over the Sea of Japan – all 12 crewmembers perished (their bodies were not recovered).
- 13 July 1952: A Soviet MiG-15 flown by Captain Osinskiy shot down a DC-3 reconnaissance plane of the Swedish Air Force piloted by Alvar Almeberg near Ventspils over the Baltic Sea. Its three crewmembers perished.
- 7 August 1952: Two MiG-15 pilots, 1st Lieutenants Zeryakov and Lesnov shot down a USAF RB-29 over the Kurile islands – all the crew of nine died (the remains of one of them, Captain John R. Durnham, was returned to the United States in 1993).
- 18 November 1952: four MiG-15bis engaged four F9F-2 Panther off the aircraft carrier USS Princeton near Vladivostok. One MiG-15 pilot, Captain Dmitriy Belyakov, manages to seriously damage Lieutenant Junior Grade David M. Rowlands' F9F-2, but seconds later he and 1st Lieutenant Vandalov were downed by Elmer Royce Williams and John Davidson Middleton; neither Soviet is found.
- March 10 1953: Two MiG-15bis of the Czechoslovak Air Force intercepted two F-84Gs over Czechoslovak airspace, and Jaroslav Sramek shot down one of them. The Thunderjet pilot bailed out safely.
- 29 July 1953: Two MiG-15bis intercepted a RB-50G near Gamov, in the Sea of Japan, and instructed them to land on their home base. The RB-50 gunners opened fire and hit the MiG of 1st Lieutenant Aleksandr D. Rybakov. Rybakov and his wingman 1st Lieutenant. Yuriy M. Yablonskiy then shot down the RB-50. One of the crewmemebers (John E. Roche) was rescued alive, and corpses of other three were recovered. The remaining 13 crew members became missing.
- 17 April 1955: The MiG-15 pilots Korotkov and Sazhin shot down an RB-47E north of the Kamchatka peninsula – all three crewmembers perished.
Suez Canal Crisis (1956)
Egypt bought a handful of MiG-15bis and MiG-17 fighters in 1955 from Czechoslovakia with the sponsorship and support of the USSR, just in time to participate in the Suez Canal Crisis. During the air combat against the Israeli Air Force the Egyptian MiG-15bis's managed to shoot down at least three Israeli aircraft in spite of suffering several losses: a Piper Cub and a Meteor F.8 on 30 October 1956, and a Dassault Ouragan on 1 November which then performed a belly landing – this last victory was scored by the Egyptian pilot Faruq el-Gazzavi.
Throughout the 1950s MiG-15s of China's People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) frequently engaged Republic of China (ROC) and U.S. aircraft in combat; in 1958, a ROC fighter achieved the first air-to-air kill with an AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missile against a PLAAF MiG-15.
The first Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin was killed in a crash during a March 1968 training flight in a MiG-15UTI due to poor visibility and miscommunication with ground control.
Production
The USSR built around 12,000 MiG-15s in all variants. It was also built under license in Czechoslovakia (as the S-102 and S-103) and Poland (as the Lim-1 and Lim-2 and biplace SB Lim-1 and SB Lim-2).
In the early 1950s, the Soviet Union delivered hundreds of MiG-15s to China, where they received the designation J-2. The Soviets also sent almost a thousand MiG-15 engineers and specialists to China, where they assisted China's Shenyang Aircraft Factory in building the MiG-15UTI trainer (designated JJ-2). China never produced a single-seat fighter version, only the two-seat JJ-2.
The designation "J-4" is unclear; some sources claim Western observers mistakenly labelled China's MiG-15bis a "J-4", while the PLAAF never used the "J-4" designation. Others claim "J-4" is used for MiG-17F, while "J-5" is used for MiG-17PF. Another source claims the PLAAF used "J-4" for Soviet-built MiG-17A, which were quickly replaced by license-built MiG-17Fs (J-5s). What is certain is, the service lives of the J-2 and J-4 in the PLAAF were short, as they were quickly replaced by the more capable J-5 and J-6.
Variants
- I-310 : Prototype.
- MiG-15 : First production version.
- MiG-15P : Single-seat all-weather interceptor version of the MiG-15bis.
- MiG-15SB : Single-seat fighter bomber version.
- MiG-15SP-5 : Two-seat all-weather interceptor version of the MiG-15UTI.
- MiG-15T : Target-towing version.
- MiG-15bis : Improved single-seat fighter version.
- MiG-15bisR : Single-seat reconnaissance version.
- MiG-15bisS : Single-seat escort fighter version.
- MiG-15bisT : Single-seat target-towing version.
- MiG-15UTI : Two-seat dual-control jet trainer.
- J-2 : Chinese designation of the MiG-15 single-seat fighter.
- JJ-2 : Chinese designation of the MiG-15UTI two-seat jet trainer.
- J-4 : Chinese designation
- Lim-1 : MiG-15 jet fighters built under license in Poland.
- Lim-1A : Polish-built reconnaissance version of the MiG-15 with AFA-21 camera.
- Lim-2 : MiG-15bis built under license in Poland, with Lis-2 (license VK-1) engines.
- Lim-2R : Polish-built reconnaissance version of MiG-15bis with a place for a camera in the front part of the canopy.
- SB Lim-1 : Polish Lim-1 converted to equivalent of MiG-15UTI jet trainers, with RD-45 jet engines.
- SB Lim-2 : Polish Lim-2 or SBLim-1 converted to jet trainers with Lis-1 (VK-1) jet engines.
- SBLim-2A or -2Art: Polish-built two-seat reconnaissance version, for correcting artillery.
- S-102 : MiG-15 jet fighters built under license in Czechoslovakia.
- S-103 : MiG-15bis jet fighters built under license in Czechoslovakia.
- CS-102 : MiG-15UTI jet trainers built under license in Czechoslovakia.
- Raduga KS-1 Komet : An Air launched anti-shipping cruise missile.
Operators
|
|
Survivors
Many MiG-15s are on display through the world. In addition, they are becoming increasingly common as private sport planes and warbirds.
- MiG-15 (s/n 2015357) is on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio. This is the aircraft flown to Kimpo Air Base in South Korea on 21 September 1953 by a defecting North Korean pilot who was given a reward of $100,000 (see above). The aircraft was flight-tested on Okinawa and then brought to the U.S. to be returned to its "rightful owners" (believed to be the Soviet Union, which denied participating in the Korean conflict)[38]. When this offer was ignored it was transferred to the United States Air Force Museum in November 1957.[46] It is on display in the Museum's Modern Flight gallery.
- There is a surviving example on display at the Fleet Air Arm Museum, UK.
Specifications (MiG-15bis)
General characteristics
- Crew: MiG-15bis=1, MiG-15UTI=2
- Length: 10.11 m (33 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 10.08 m (33 ft 1 in)
- Height: 3.70 m (12 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 20.6 m² (221.74 ft²)
- Airfoil: TsAGI S-10 / TsAGI SR-3
- Empty weight: 3,580 kg (7,900 lb)
- Loaded weight: 4,960 kg (10,935 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 6,105 kg (13,460 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 1,400 L (364 US gal))
- Powerplant: 1× Klimov VK-1 turbojet, 26.5 kN (5,950 lbf)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,075 km/h (668 mph)
- Cruise speed: 840 km/h (520 mph)
- Range: 1,200 km, 1,975 km with external tanks (745 mi / 1,225 mi)
- Service ceiling: 15,500 m (50,850 ft)
- Rate of climb: 50 m/s (9,840 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 240.8 kg/m² (49.3 lb/ft²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.54
Armament
- 2x NR-23 23mm cannons in lower left fuselage(80 rounds per gun, 160 rounds total)
- 1x Nudelman N-37 37 mm cannon in lower right fuselage (40 rounds total)
- 2x 100 kg (220 lb) bombs, drop tanks, or unguided rockets on underwing hardpoints.
See also
Related development
Comparable aircraft
- Focke-Wulf Ta 183
- FMA IAe 33 Pulqui II
- F-84 Thunderjet
- F-86 Sabre
- Lavochkin La-15
- Dassault Ouragan
- Saab 29 Tunnan
Related lists










0 comments:
Post a Comment